Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Masahiko; Horigome, Kazushi; Kuno, Takehiko
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 190, p.110460_1 - 110460_7, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.61(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Gravimetric measurement of U content in UO with ignition in the air has been investigated. The ignition temperature, ignition time and aliquot sample mass are optimized as 900
with ignition in the air has been investigated. The ignition temperature, ignition time and aliquot sample mass are optimized as 900 C, 60 minutes, and 1 g, respectively. The method is validated by IDMS with uncertainty estimation. The obtained result by gravimetry is 0.78236
C, 60 minutes, and 1 g, respectively. The method is validated by IDMS with uncertainty estimation. The obtained result by gravimetry is 0.78236 0.00051 g/g (k=2) and agreed with IDMS value within its uncertainty. It has been found that U in UO
0.00051 g/g (k=2) and agreed with IDMS value within its uncertainty. It has been found that U in UO can be measured accurately and precisely by gravimetry.
can be measured accurately and precisely by gravimetry.
Uehara, Akihiro*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Ikeda, Atsushi; Numako, Chiya*; Terada, Yasuko*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Ina, Toshiaki*; Takeda-Homma, Shino*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 559, p.153422_1 - 153422_11, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Segawa, Tomoomi; Kawaguchi, Koichi; Ishii, Katsunori; Suzuki, Masahiro; Tachihara, Joji; Takato, Kiyoto; Okita, Takatoshi; Satone, Hiroshi*; Suzuki, Michitaka*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 8(3), p.21-00022_1 - 21-00022_9, 2021/06
To reduce the hold-up of the nuclear fuel materials in the glove box and the external exposure dose, the technology of the MOX powder adhesion prevention by the nanoparticle coating to the acrylic panels of the glove box has been developed. The surface analysis by means of atomic force microscopy (AFM) showed that the acrylic test piece surface coated with nanoparticles had a higher root mean square roughness value than that non-coated with nanoparticles. Due to the formation of nano-sized tiny rugged surface, the nanoparticle coating reduced the minimum adhesion force between the UO particles and the acrylic test piece surface with the smallest particle size of about 5
particles and the acrylic test piece surface with the smallest particle size of about 5  m where desorption was observed, by about one-tenth. Moreover, the nanoparticle coating reduced the amount of the MOX powder adhering to the acrylic test piece to about one-tenth. In this study, it was found that applying the nanoparticle coating to the acrylic panels of glove box can prevent the adhesion of nuclear fuel materials. This method is effective for reducing the hold-up of the nuclear fuel materials in the glove box, the external exposure dose and improving the visibility of the acrylic panels.
m where desorption was observed, by about one-tenth. Moreover, the nanoparticle coating reduced the amount of the MOX powder adhering to the acrylic test piece to about one-tenth. In this study, it was found that applying the nanoparticle coating to the acrylic panels of glove box can prevent the adhesion of nuclear fuel materials. This method is effective for reducing the hold-up of the nuclear fuel materials in the glove box, the external exposure dose and improving the visibility of the acrylic panels.
Segawa, Tomoomi; Kawaguchi, Koichi; Ishii, Katsunori; Suzuki, Masahiro; Tachihara, Joji; Takato, Kiyoto; Okita, Takatoshi; Satone, Hiroshi*; Suzuki, Michitaka*
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/08
To reduce the hold-up of the nuclear fuel materials in the glove box and the external exposure dose, the technology of the MOX powder adhesion prevention by the nanoparticle coating to the acrylic panels of the glove box has been developed. Due to the formation of nano-sized tiny rugged surface, the nanoparticle coating reduced the minimum adhesion force between the UO particles and the acrylic test piece surface with the smallest particle size of about 5
particles and the acrylic test piece surface with the smallest particle size of about 5  m where desorption was observed, by about one-tenth. Moreover, the nanoparticle coating reduced the amount of the MOX powder adhering to the acrylic test piece to about one-tenth. In this study, it was found that applying the nanoparticle coating to the acrylic panels of glove box can prevent the adhesion of nuclear fuel materials. This method is effective for reducing the hold-up of the nuclear fuel materials in the glove box, the external exposure dose and improving the visibility of the acrylic panels.
m where desorption was observed, by about one-tenth. Moreover, the nanoparticle coating reduced the amount of the MOX powder adhering to the acrylic test piece to about one-tenth. In this study, it was found that applying the nanoparticle coating to the acrylic panels of glove box can prevent the adhesion of nuclear fuel materials. This method is effective for reducing the hold-up of the nuclear fuel materials in the glove box, the external exposure dose and improving the visibility of the acrylic panels.
 -radiation and H
-radiation and H O
O induced oxidative dissolution of uranium(IV) oxide in aqueous solution containing phthalic acid
induced oxidative dissolution of uranium(IV) oxide in aqueous solution containing phthalic acidKumagai, Yuta; Jonsson, M.*
Dalton Transactions (Internet), 49(6), p.1907 - 1914, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)This study aims to reveal possible involvements of organic acids in the oxidative dissolution of UO . Using phthalic acid as a model compound, we have measured adsorption on UO
. Using phthalic acid as a model compound, we have measured adsorption on UO and investigated effects on the reaction between H
and investigated effects on the reaction between H O
O and UO
and UO and on oxidative dissolution induced by
and on oxidative dissolution induced by  -irradiation. Significant adsorption of phthalic acid was observed even at neutral pH. However, the reaction between H
-irradiation. Significant adsorption of phthalic acid was observed even at neutral pH. However, the reaction between H O
O and UO
and UO in phthalic acid solution induced oxidative dissolution of U(VI) similarly to aqueous bicarbonate solution. These results indicate that even though phthalic acid adsorbs on the UO
in phthalic acid solution induced oxidative dissolution of U(VI) similarly to aqueous bicarbonate solution. These results indicate that even though phthalic acid adsorbs on the UO surface, it is not involved in the interfacial reaction by H
surface, it is not involved in the interfacial reaction by H O
O . In contrast, the dissolution of U by irradiation was inhibited in aqueous phthalic acid solution, whereas H
. In contrast, the dissolution of U by irradiation was inhibited in aqueous phthalic acid solution, whereas H O
O generated by radiolysis was consumed by UO
generated by radiolysis was consumed by UO . The inhibition suggests that radical species derived from phthalic acid was involved in the redox reaction process of UO
. The inhibition suggests that radical species derived from phthalic acid was involved in the redox reaction process of UO .
.
 O
O concentration on oxidative dissolution of U
concentration on oxidative dissolution of U O
OKumagai, Yuta
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (107), p.77 - 78, 2019/04
Reaction of hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) with uranium dioxide (UO
) with uranium dioxide (UO ) oxidizes U(IV) to water-soluble U(VI). In the concept of direct geological disposal of spent nuclear fuel, this reaction is expected to induce dissolution of UO
) oxidizes U(IV) to water-soluble U(VI). In the concept of direct geological disposal of spent nuclear fuel, this reaction is expected to induce dissolution of UO matrix of the spent fuel. This study investigate effect of H
matrix of the spent fuel. This study investigate effect of H O
O concentration on the kinetics and the yield of U(VI) dissolution of this reaction. A series of experiments of the reaction of H
concentration on the kinetics and the yield of U(VI) dissolution of this reaction. A series of experiments of the reaction of H O
O with UO
with UO powder dispersed in water has been carried out. The experimental results reveal that increase in the H
powder dispersed in water has been carried out. The experimental results reveal that increase in the H O
O concentration slows down the reaction and decreases the yield of U(VI) dissolution. This observation suggests that a reaction intermediate is generated in the course of the H
concentration slows down the reaction and decreases the yield of U(VI) dissolution. This observation suggests that a reaction intermediate is generated in the course of the H O
O reaction on the surface of UO
reaction on the surface of UO .
.
 induced by H
induced by H O
O and
and  -irradiation
-irradiationKumagai, Yuta; Fidalgo, A. B.*; Jonsson, M.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 123(15), p.9919 - 9925, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:62.54(Chemistry, Physical)Radiation-induced oxidative dissolution of uranium dioxide (UO ) is one of the most important chemical processes of U driven by redox reactions. We have examined the effect of UO
) is one of the most important chemical processes of U driven by redox reactions. We have examined the effect of UO stoichiometry on the oxidative dissolution of UO
stoichiometry on the oxidative dissolution of UO induced by hydrogen peroxide (H
induced by hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) and
) and  -ray irradiation. By comparing the reaction kinetics of H
-ray irradiation. By comparing the reaction kinetics of H O
O between stoichiometric UO
between stoichiometric UO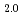 and hyper-stoichiometric UO
and hyper-stoichiometric UO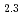 , we observed a significant difference in reaction speed and U dissolution kinetics. The stoichiometric UO
, we observed a significant difference in reaction speed and U dissolution kinetics. The stoichiometric UO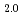 reacted with H
reacted with H O
O much faster than the hyper-stoichiometric UO
much faster than the hyper-stoichiometric UO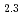 . The U dissolution from UO
. The U dissolution from UO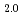 was initially much lower than that from UO
was initially much lower than that from UO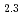 , but gradually increased as the oxidation by H
, but gradually increased as the oxidation by H O
O proceeded. The
proceeded. The  -ray irradiation induced the U dissolution that is analogous to the kinetics by the exposure to a low concentration (0.2 mM) of H
-ray irradiation induced the U dissolution that is analogous to the kinetics by the exposure to a low concentration (0.2 mM) of H O
O . The exposure to higher H
. The exposure to higher H O
O concentrations caused lower U dissolution and resulted in deviation from the U dissolution behavior by
concentrations caused lower U dissolution and resulted in deviation from the U dissolution behavior by  -ray irradiation.
-ray irradiation.
 O
O and UO
and UO
Fidalgo, A. B.*; Kumagai, Yuta; Jonsson, M.*
Journal of Coordination Chemistry, 71(11-13), p.1799 - 1807, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:88.5(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In this work, we have studied the reaction between H O
O and UO
and UO with particular focus on the nature of the hydroxyl radical formed as an intermediate. Experiments were performed to study the kinetics of the reaction at different initial H
with particular focus on the nature of the hydroxyl radical formed as an intermediate. Experiments were performed to study the kinetics of the reaction at different initial H O
O concentrations. The results show that the consumption rates at a given H
concentrations. The results show that the consumption rates at a given H O
O concentration are different depending on the initial H
concentration are different depending on the initial H O
O concentration. This is attributed to an alteration of the reactive interface, likely caused by blocking of surface sites by oxidized U/surface-bound hydroxyl radicals. The U dissolution yield decreases with increasing initial H
concentration. This is attributed to an alteration of the reactive interface, likely caused by blocking of surface sites by oxidized U/surface-bound hydroxyl radicals. The U dissolution yield decreases with increasing initial H O
O concentration. This is expected from the mechanism of catalytic decomposition of H
concentration. This is expected from the mechanism of catalytic decomposition of H O
O on oxide surfaces. As the experiments were performed in solutions containing 10 mM and a strong concentration dependence was observed in the 0.2 - 2.0 mM H
on oxide surfaces. As the experiments were performed in solutions containing 10 mM and a strong concentration dependence was observed in the 0.2 - 2.0 mM H O
O concentration range, we conclude that the intermediate hydroxyl radical is surface bound rather than free.
concentration range, we conclude that the intermediate hydroxyl radical is surface bound rather than free.
 to obtain the high U solution
to obtain the high U solution; *; Sakurai, Koji*; ; Nomura, Kazunori; *
JNC TN8400 2000-032, 98 Pages, 2000/12
Concerning the preparation of high U solution for the crystallization process and the application of UO powder dissolution to that, the effects of final U concentration, dissolution temperature, nitric acid concentration and powder size on the dissolution of UO
powder dissolution to that, the effects of final U concentration, dissolution temperature, nitric acid concentration and powder size on the dissolution of UO powder in the nitric acid where the final U concentration was
powder in the nitric acid where the final U concentration was  800g/L were investigated. The experimental results showed that the solubility of UO
800g/L were investigated. The experimental results showed that the solubility of UO decreased with the increase of final UO
decreased with the increase of final UO concentration and powder size, and with the decrease of dissolution temperature and nitric acid concentration. It was also confirmed that in the condition where the final U concentration was sufficiently lower than the solubility of U, UO
concentration and powder size, and with the decrease of dissolution temperature and nitric acid concentration. It was also confirmed that in the condition where the final U concentration was sufficiently lower than the solubility of U, UO dissolution behavior in the high U solution could be estimated with the equation based on the fragmentation model which we had already reported. Based on these experimental results, the dissolution behavior of irradiated MOX fuel in high U solution was estimated and the possibility of supplying high U solution to the crystallization process was discussed. In the preparation of high U solution for the crystallization process, it was estimated that the present dissolution process (dissolution for fuel pieces of about 3cm long) needed a lot of time to obtain a high dissolution yield, but it was shorted drastically by the pulverization of fuel pieces. The burst of off-gas at the early in the dissolution of fuel powder seems to be avoidable with setting the appropriate dissolution condition, and it is important to optimize the dissolution condition with considering the capacity of off-gas treatment process.
dissolution behavior in the high U solution could be estimated with the equation based on the fragmentation model which we had already reported. Based on these experimental results, the dissolution behavior of irradiated MOX fuel in high U solution was estimated and the possibility of supplying high U solution to the crystallization process was discussed. In the preparation of high U solution for the crystallization process, it was estimated that the present dissolution process (dissolution for fuel pieces of about 3cm long) needed a lot of time to obtain a high dissolution yield, but it was shorted drastically by the pulverization of fuel pieces. The burst of off-gas at the early in the dissolution of fuel powder seems to be avoidable with setting the appropriate dissolution condition, and it is important to optimize the dissolution condition with considering the capacity of off-gas treatment process.
Tejima, Shogo
JNC TN8400 2000-029, 54 Pages, 2000/10
This report describes the study done by the author as a postdoctoral research associate at Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute. This report is divided into three parts: construction of a relativistic band calculation formalism based on the density functional theory, using this method, investigation of the electrical properties for ferromagnetic UGe and antiferromagnetic UO
and antiferromagnetic UO . (1)A relativistic band calculation (RBC) method. Band calculations for the s, p, and d electric structure have been developed well in the practical application and theoretical study. But band calculation method treating magnetic 5f electrons as actinide compounds are complicated and needed relativistic approach, so it is behind with the study of the 5f system. In this study we construct the relativistic band calculationformalism valid for magnetic 5f electrons. (2)Electric properties of UGe
. (1)A relativistic band calculation (RBC) method. Band calculations for the s, p, and d electric structure have been developed well in the practical application and theoretical study. But band calculation method treating magnetic 5f electrons as actinide compounds are complicated and needed relativistic approach, so it is behind with the study of the 5f system. In this study we construct the relativistic band calculationformalism valid for magnetic 5f electrons. (2)Electric properties of UGe . The actinide compounds UGe
. The actinide compounds UGe is ferromagnetic, so the theoretical analysis is not well yet. The electric structure and fermi surface of UGe
is ferromagnetic, so the theoretical analysis is not well yet. The electric structure and fermi surface of UGe are analyzed using the RBC. The theoretical results show that UGe
are analyzed using the RBC. The theoretical results show that UGe is heavy electron with the 5f character and are agreement with experimental one. (3)Electric structure of nuclear fuel UO
is heavy electron with the 5f character and are agreement with experimental one. (3)Electric structure of nuclear fuel UO . It is important to understand the mechanism of the thermal conductivity of nuclear fuel as antiferromagnetic UO
. It is important to understand the mechanism of the thermal conductivity of nuclear fuel as antiferromagnetic UO . The UO
. The UO band calculation reflecting the thermal properties, into account of relativistic effect, have not done yes. So using the RBC the detailed electric structure of UO
band calculation reflecting the thermal properties, into account of relativistic effect, have not done yes. So using the RBC the detailed electric structure of UO are obtained.
are obtained.
Sugino, Kazuteru; Iwai, Takehiko*;
JNC TN9400 2000-098, 182 Pages, 2000/07
In order to support the Russian excess weapons plutonium disposition, the international collaboration has been started between Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) and Russian Institute of Physics and Power Engineering (IPPE). In the frame of the collaboration, JNC has carried out analyses on the BFS-62 assemblies that are constructed in the fast reactor critical experimental facility BFS-2 of IPPE. This report summarizes an experimental analysis on the BFS-62-1 assembly, which is the first core of the BFS-62 series. The core contains the enriched U0 fuel surrounded by the U0
fuel surrounded by the U0 blanket. The standard analytical method for fast reactors has been applied, which was used for the JUPITER and other experimental analyses. Due to the lack of the analytical data the 2D RZ core calculation was mainly used. The 3D XYZ core calculation was applied only for the preliminary evaluation. Further in terms of the utilization of the BFS experimental analysis data for the standard data base for FBR core design, consistency evaluation with JUPITER experimental analysis data has been performed using the cross-section adjustment method. As the result of analyses, good agreement was obtained between calculations and experiments for the criticality and the reaction rate ratio. However, it was found that accurate evaluation of the reaction rate distribution was impossible without exact consideration of the arrangement of the two types of sodium (with and without hydrogen impurity), which can be accommodated by the 3D core analysis, thus it was essentia1. In addition, it was clarifie that there was a room for an improvement of the result on the reaction rate distribution in the blanket and shielding regions. The application of the 3D core calculation improved the result on the control rod worth because 3D core model can more exactly consider the shape of the control rod. Furthermore it was judged that the result of the analysis on the sodium void reactivity .....
blanket. The standard analytical method for fast reactors has been applied, which was used for the JUPITER and other experimental analyses. Due to the lack of the analytical data the 2D RZ core calculation was mainly used. The 3D XYZ core calculation was applied only for the preliminary evaluation. Further in terms of the utilization of the BFS experimental analysis data for the standard data base for FBR core design, consistency evaluation with JUPITER experimental analysis data has been performed using the cross-section adjustment method. As the result of analyses, good agreement was obtained between calculations and experiments for the criticality and the reaction rate ratio. However, it was found that accurate evaluation of the reaction rate distribution was impossible without exact consideration of the arrangement of the two types of sodium (with and without hydrogen impurity), which can be accommodated by the 3D core analysis, thus it was essentia1. In addition, it was clarifie that there was a room for an improvement of the result on the reaction rate distribution in the blanket and shielding regions. The application of the 3D core calculation improved the result on the control rod worth because 3D core model can more exactly consider the shape of the control rod. Furthermore it was judged that the result of the analysis on the sodium void reactivity .....
Kakehi, Isao;
JNC TN9400 2000-054, 84 Pages, 2000/04
This report describes accomplishment of the study on the quality of vipac (vibro-packed) oxide fuel obtained by pyrochemical processing (molten salt electrolytic processing). This study is intended to contribute to the design study of the pyro-reprocessing-vipac fuel recycling system of oxide fuel. In this study, vibro-packing experiment has been conducted using granular U0 obtained by molten salt electrolytic processing (cold experiment). The oxide pyro process developed by Research lnstitute of Atomic Reactors (RIAR) is the method in which the sintered oxide is electrically deposited on the cathode at approximately 600
obtained by molten salt electrolytic processing (cold experiment). The oxide pyro process developed by Research lnstitute of Atomic Reactors (RIAR) is the method in which the sintered oxide is electrically deposited on the cathode at approximately 600 C. 0xide granules for vipac fuel are obtained by crushing the oxide deposited on the cathode. This process is also developed as recycle process because it is capable of FP separation. Also in Japan, this process is studied as one of the new FBR fuel recycling systems. ln this study, we made an effort to clarify the mechanisms of vibro-packing of the electrically obtained granules, which influence on the effective parameters of vibro-packing density and fuel particles size distribution in the fuel cladding in case of non-sphere particles of the granules. As a result of the study, smear density of 75% and almost uniform distribution of U0
C. 0xide granules for vipac fuel are obtained by crushing the oxide deposited on the cathode. This process is also developed as recycle process because it is capable of FP separation. Also in Japan, this process is studied as one of the new FBR fuel recycling systems. ln this study, we made an effort to clarify the mechanisms of vibro-packing of the electrically obtained granules, which influence on the effective parameters of vibro-packing density and fuel particles size distribution in the fuel cladding in case of non-sphere particles of the granules. As a result of the study, smear density of 75% and almost uniform distribution of U0 particles have been taken in the experiment, and much knowledge for the improvement of the vibro-packing quality has been found. And the possibility of the smear density over 80% and the uniform distribution of U0
particles have been taken in the experiment, and much knowledge for the improvement of the vibro-packing quality has been found. And the possibility of the smear density over 80% and the uniform distribution of U0 particles has been suggested in this study.
particles has been suggested in this study.
Yamanaka, Shinsuke*; Uno, Masayoshi*; Kurosaki, Ken*; ; Namekawa, Takashi
JNC TY9400 2000-011, 41 Pages, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
*; *; *; *
JNC TJ9440 2000-007, 43 Pages, 2000/03
Planning of the plutonium utihzation in the Light water thermal reactor has been investigated to evaluate scenario for FBR development. Plans for MOX fuel utilization in the ABWR including Ooma plant are studied, and information of high burnup fuels for a future BWR is summarized based on public documents. Nuclear compositions of the present burnup fuel (45,000MWd/t) and a high burnup fue (60,000MWd/t) have been evaluated using an open code: SRAC. Results of the study are follows; (1)Surveying the status of MOX fuel utilization. The status of MOX and UO fuel utilization in the present BWR and future BWR have been summarized based on public documents. (2)Evaluation of spent MOX and UO
fuel utilization in the present BWR and future BWR have been summarized based on public documents. (2)Evaluation of spent MOX and UO fuel composition. Nuclear compositions of spent MOX and UO
fuel composition. Nuclear compositions of spent MOX and UO fuels at 45,000MWd/t and 60,000MWd/t burnup have been evaluated and summarized for recycle scenarios by FBR.
fuels at 45,000MWd/t and 60,000MWd/t burnup have been evaluated and summarized for recycle scenarios by FBR.
Morita, Koji; Tobita, Yoshiharu; kondo, Satoru; E.A.Fischer*
JNC TN9400 2000-005, 57 Pages, 1999/05
An improved analytic equation-of-state (EOS) model using flexible thermodynamic functions is developed for a reactor safety analysis code, SIMMER-III. The present EOS model is designed to have adequate accuracy in describing thermodynamic properties of reactor-core materials over wide temperature and pressure ranges and to consistently satisfy basic thermodynamic relationships without deterioration of the computing efficiency. The fluid-dynamic algorithm for pressure iteration consistently coupled with the EOS model is also described in the present report. The EOS data of the basic core materials, uranium dioxide, mixed-oxide fuel, stainless steel, and sodium, are developed up to the critical point by compiling the most up-to-date and reliable sources using basic thermodynamic relationships. The thermodynamic consistency and accuracy of the evaluated EOS data are also discussed by comparison with the available sources.
Morita, Koji; Tobita, Yoshiharu; kondo, Satoru; E.A.Fischer*
JNC TN9400 2000-004, 38 Pages, 1999/05
An analytic thermophysical property model using general function forms is developed for a reactor safety analysis code, SIMMER-III. The function forms arc designed to represent correct behavior of properties of reactor-core materials over wide temperature ranges, especially for the thermal conductivity and the viscosity near the critical point. The most up-to-date and reliable sources for uranium dioxide, mixed-oxide fuel, stainless stee1, and sodium available at present are used to determine parameters in the proposed functions. This model is also designed to be consistent with a SIMMER-III model on thermodynamic properties and equations of state for reactor-corc materials.
Saito, Hioraki*; Iriya, Yoshikazu*
JNC TJ8440 99-003, 156 Pages, 1999/03
no abstracts in English
Brear, D. J.
PNC TN9410 98-005, 53 Pages, 1998/01
When liquid fuel makes contact with steel structure the liquid can freeze as a crust and the structure can melt at the surface. The melting and freezing processes that occur can influence the mode of fuel freezing and hence fuel relocation. Furthermore the temperature gradients established in the fuel and steel phases determine the rate at which heat is transferred from fuel to steel. In this memo the 1-D transient heat conduction equations are applied to the case of initially liquid UO brought into contact with solid steel using up-to-date materials properties. The solutions predict criteria for fuel crust formation and steel melting and provide a simple algorithm to determine the interface temperature when one or both of the materials is undergoing phase change. The predicted steel melting criterion is compared with available experimental results.
brought into contact with solid steel using up-to-date materials properties. The solutions predict criteria for fuel crust formation and steel melting and provide a simple algorithm to determine the interface temperature when one or both of the materials is undergoing phase change. The predicted steel melting criterion is compared with available experimental results.
; Hirosawa, Takashi
PNC TN9410 97-075, 20 Pages, 1997/08
Fuel melting temperature is one of the major thermodynamical properties that is used for determining the design criteria on fuel temperature during irradiation in FBR. In general, it is necessary to evaluate the correlation of fuel melting temperature to confirm that the fuel temperature must be kept below the fuel melting temperature during irradiation at any conditions. The correlations of the melting temperature of uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel, typical FBR fuel, used to be estimated and formulized based on the measured values reported in 1960's and has been applied to the design. At present, some experiments have been accumulated with improved experimental techniques. And it reveals that the recent measured melting temperatures does not agree well to the data reported in 1960's and that some of the 1960's data should be modified by taking into account of the recent measurements. In this study, the experience of melting temperature up to now are summarized and evaluated in order to make the fuel pin design more reliable. The effect of plutonium content, oxygen to metal ratio and burnup on MOX fuel melting was examined based on the recent data under the UO - PuO
- PuO - PuO
- PuO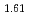 ideal solution model, and then formulized. The correlation obtained in this work is as-follows; T = T
ideal solution model, and then formulized. The correlation obtained in this work is as-follows; T = T +
+  T
T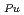 +
+  T
T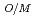 +
+  T
T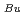 ----(A) T
----(A) T = 3120
= 3120  T
T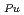 = -5.7537
= -5.7537 PU + 1.3631
PU + 1.3631 10
10
 PU
PU + 1.7952
+ 1.7952 10
10
 PU
PU
 T
T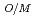 = -1.41
= -1.41  PU
PU  (2.00 - OP)/0.39 OP : OP =
(2.00 - OP)/0.39 OP : OP = 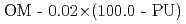 /(0.01
/(0.01 PU)
PU)  T
T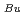 = -5.0
= -5.0 BU/10000 where T is the melting temperature (degree of K), PU is the weight fraction of PuO
BU/10000 where T is the melting temperature (degree of K), PU is the weight fraction of PuO in the mixed oxide fuel, OM is the oxygen to metal ratio, and BU is the burnup in the unit of MWd/MTM. respectively.
in the mixed oxide fuel, OM is the oxygen to metal ratio, and BU is the burnup in the unit of MWd/MTM. respectively.  T
T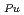 (plutonium content),
(plutonium content),  T
T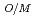 (O/M Ratio),
(O/M Ratio),  ...
...